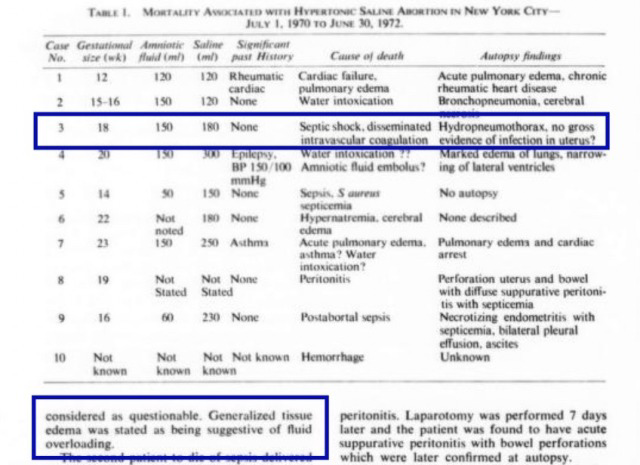
A study published in the Obstetrics and Gynecology medical journal documented 10 cases of maternal death from legal saline abortions in New York City. All of the women in the study had undergone their abortions thanks to New York’s pre-Roe legalization and had died between July 1, 1970 and June 30, 1972.
While nine of the cases appear to match some of those documented in another study, the person who was given the designation “Case 3” did not appear to match any known report. (She is given the pseudonym “Phyllis” here to avoid dehumanizing her by reducing her to a number.) In addition, her postmortem findings were found to be suspicious considering the listed cause of death.
“Phyllis” underwent her saline abortion at approximately 18 weeks pregnant. The hazardous method was performed by a New York City hospital, apparently as an outpatient procedure. After receiving the hypertonic saline injections, she was discharged.
The next day, Phyllis returned to the hospital with a fever of 104 degrees. After delivering her dead child, she continued to bleed. Vacuum aspiration was performed and the hospital began treating her for septic shock and abnormally decreased urine output.
Even though she had been healthy with no history of serious illness, Phyllis died in three days. Her postmortem report showed peculiar results that cast doubt on whether or not her complications had been diagnosed and treated correctly.
Even though Phyllis’s diagnosis during her hospitalization had been septic shock, her blood cultures showed no growth at all. Cervical cultures were reported to have grown “multiple organisms,” but did not list what organisms, whether or not they were infectious or which species were likely to have caused her death. Her uterus, which would most likely have been the site of initial infection, had “no gross evidence of infection” and there was a note that “microscopic preparations were not available”— very strange for an in-hospital death supposedly from infection.
Phyllis had both air and fluid in her pleural space. She had been suffering from generalized tissue edema which was stated as “being suggestive of fluid overloading.” Despite all of these findings (and in some cases lack of them), her cause of death was still given as sepsis.
The study that later recorded Phyllis’s death regarded the autopsy findings with some degree of skepticism. While the study listed the diagnosis of sepsis as her cause of death, the authors wrote that “the description of [her] uterus must be considered as questionable.”
Analysis
What really happened to Phyllis? While at this point it may be impossible to know for sure, there are several possible explanations for the suspicious postmortem findings. One is that she really did die of sepsis, but that the lab work was mishandled. If, as the study noted, the description of her uterus was questionable, it could be possible that it was simply poorly examined.
Another possibility is that Phyllis was misdiagnosed and that the hospital decided to list her cause of death as a match for her initial diagnosis to avoid suspicion of malpractice. That may explain why important microscopic preparations were reportedly “unavailable.”
The findings of the autopsy may also indicate that Phyllis may have suffered another complication from saline abortion: hypervolemic hypernatremia. Hypernatremia, an electrolyte imbalance from dangerous levels of salt in the body, had already been well-established to have killed saline abortion clients by the time Phyllis was killed. If this had been the case for her, it could have caused hypervolemia as her body desperately tried to hold onto fluids to regulate her osmotic levels. This is highly consistent with the observations of generalized edema and fluid overloading and could also have explained her abnormalities in urine output. She also suffered disseminated intravascular coagulopathy or DIC, a well-documented symptom in many abortion deaths involving saline in the bloodstream.(Considering that the same hospital had been responsible for the abortion and for treatment during Phyllis’s last days of life, there is a possibility that they would have an additional incentive to give her cause of death as sepsis. While still avoidable, sepsis could also have happened after birth, stillbirth or miscarriage, making a death from abortion-related sepsis seem more of an “acceptable” risk to some. However, death by hypernatremia after a massive dose of hypertonic saline in the bloodstream would not have occurred naturally for any of these, making her death without a doubt the result of the hospital’s actions.)
Yet another possibility combines some of the others: that the diagnosis of sepsis was correct and that Phyllis was suffering from undiagnosed hypernatremia. A study conducted decades after her death found correlations between hypernatremia and risk of developing sepsis. Both sepsis and hypernatremia can also cause similar problems such as kidney dysfunction, so it is possible that Phyllis died of a combination of complications. Her DIC could be explained by toxic hypertonic saline in the bloodstream, sepsis or both.
At this point it may not be possible to know for sure which exact complications killed Phyllis. What was never in doubt, however, is that she and her baby were two more preventable deaths from pre-Roe legalized abortion in New York City.
(All above images and information are from this study: Mortality Associated with Hypertonic Saline Abortion)

No comments:
Post a Comment